Our food supply depends on the world’s smallholder producers and the soils on which they farm. But soil degradation, which affects one-third of the earth’s land area, threatens farmers’ livelihoods and results in $40 billion per year in economic losses. To increase productivity, farmers must apply plant nutrients (via fertilizers) that their soils lack.
Most smallholder farmers, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, have access to fertilizers containing only primary nutrients: nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K). But crops, like humans, need a full range of nutrients for healthy growth. Analyses indicate that soils across the continent are deficient in secondary and micronutrients. According to IFDC research and field trials, addressing these deficiencies can increase yields dramatically.
Balanced crop nutrition refers to feeding crops with a balanced suite of nutrients that are lacking in the soil. Soil-SMaRT is a step-by-step framework developed by IFDC to deliver balanced fertilizers to farmers.
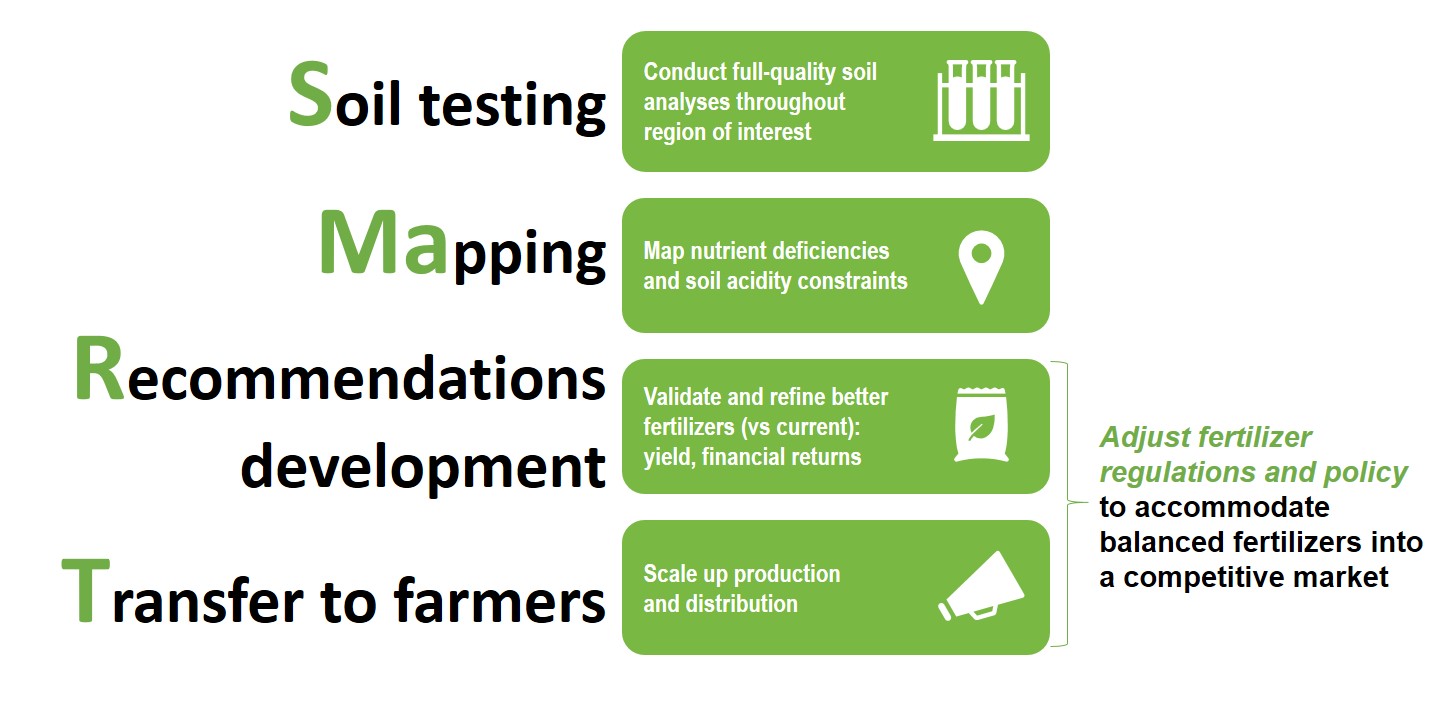
Soil testing
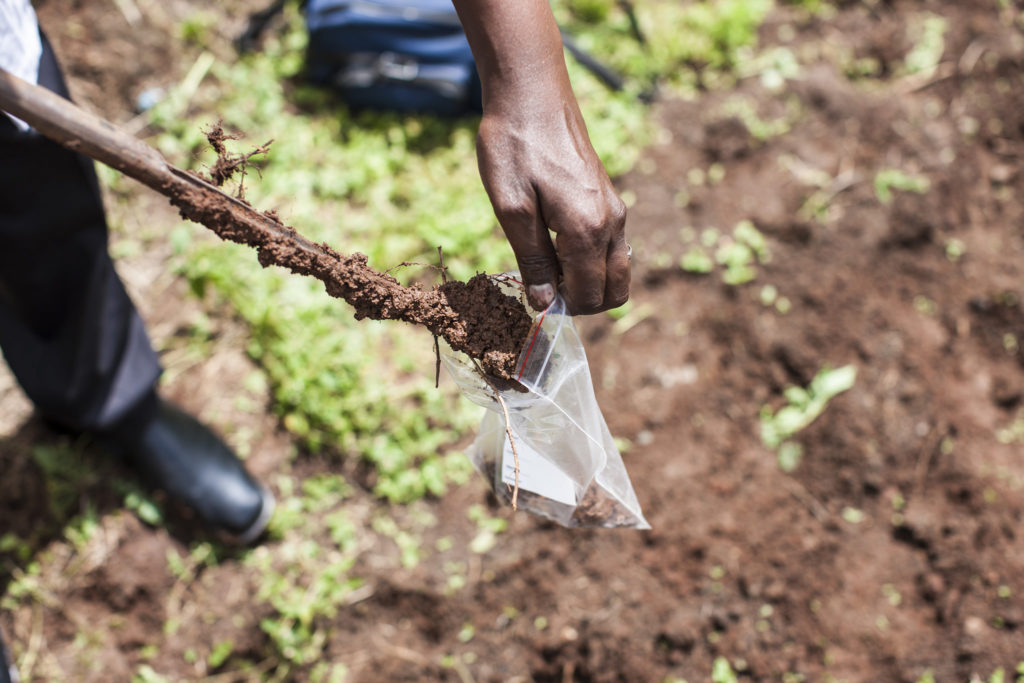
Understanding the extent of nutrient deficiencies is crucial to developing and marketing improved fertilizers. Complete soil testing by qualified laboratories can identify major nutrient gaps. These analyses must be conducted on a broad scale, using hundreds of samples that represent a wide range of agro-ecologies and soil types.
For example, through the Feed the Future Ghana Agriculture Technology Transfer project, IFDC collected soil and plant tissue samples across the three northern regions of Ghana. The samples were analyzed for their elemental (nutrient) concentrations.
Mapping
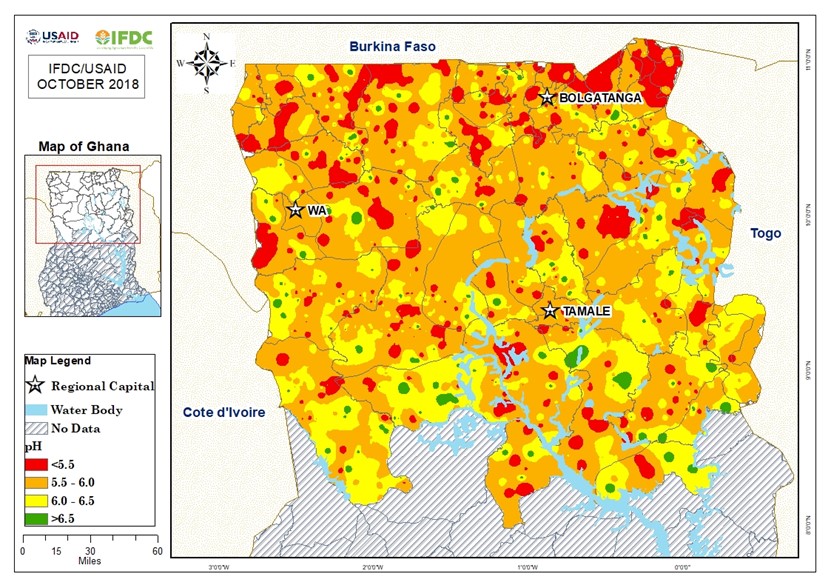
Soil nutrient and soil acidity maps serve as guides for developing crop-specific fertilizer blends that correspond to major soil types and crops. The maps help fertilizer producers understand which nutrient and acidity constraints need to be addressed. They also demonstrate to policymakers the need to accommodate multi-nutrient fertilizers into the market.
Based on soil analysis, IFDC developed soil fertility maps for northern Ghana. These maps have been continuously updated and include data on pH, organic matter, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, zinc, and boron. The soils are generally acidic to slightly acidic, and much of the land area is deficient in phosphorus, sulfur, zinc, and boron. For farmers to increase productivity in these soils and realize the full benefits of investing in fertilizer, they must have access to products containing these plant nutrients.
Recommendations development
Recommendations development involves determining which nutrients belong in specific fertilizers and the most appropriate nutrient rates. In this step, trials and field evaluations are critical for developing and evaluating fertilizer formulations. Developed products should be validated on a broad scale within the agro-ecology and with the specific crops they are intended to address.
To develop appropriate recommendations for northern Ghana, IFDC established 97 nutrient omission trials using maize as the test crop. The quantity of nutrients needed will depend on the results of nutrient omission trials, which are currently being harvested.
Technology transfer
Technology transfer involves establishing farmer demand and meeting that demand through efficient supply channels. Governments and private companies may choose many forms of advertising to promote their products, such as selling in small packs or working through extension services to increase farmer awareness.
In addition, a region’s policy and regulatory environment can help or hinder the process of bringing balanced fertilizers to farmers. Policies and regulations should be well-understood and taken into consideration in the development of new fertilizer products.
Bringing people together
Getting better fertilizer into farmers’ hands requires interaction and cooperation between key stakeholders in public and private sectors, who often do not have a history of working together. Creating collaborative mechanisms, such as fertilizer platforms, is key.
To galvanize collaboration in Ghana, IFDC held the Northern Ghana Soils and Fertilizer Forum. The event brought together agricultural producer organizations, public policymakers, private sector input providers, and other stakeholders to discuss the latest scientific information on the state of soils in the region. IFDC has held similar events in Kenya, Myanmar, and a number of other countries and regions.





